Latin America Bone Grafts and Substitutes- A Brief Analysis
 |
| Bone Grafts and Substitutes |
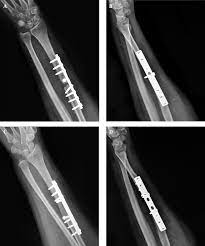
The field of orthopedics and trauma surgery has witnessed tremendous advancements in recent years. One such major area of progress is bone grafts and substitutes that are used extensively in various bone repair and reconstruction procedures.
Autografts Remain the Gold Standard
When it comes to bone grafting procedures, autografts, which involve
transplanting bone from one site to another in the same person, remain the gold
standard. The transplanted bone fuses easily and causes minimal immune response.
Despite the advancements in bone substitute technology, autografts are still
preferred in many situations given their osteoinductive and osteoconductive
properties. However, autografts do have some disadvantages like requiring
additional surgery to harvest bone, risk of donor site morbidity, and limited
supply.
Allografts Gaining Popularity
With limitations of autografts, allografts or bone grafts taken from another
human (either a cadaver or a living donor) have increased in usage. Latin
American countries have made efforts to establish proper organ and tissue banks
for sourcing allografts. However, risks of disease transmission and immune
reactions persist. To address this, allografts undergo processing like
freeze-drying, irradiation, or treatment with chemical agents to minimize
immune response. Demineralized bone matrix (DBM), an allograft material
processed to remove minerals while preserving non-collagenous proteins, is
widely used.
Xenografts Yet to Make an Impact
Xenografts involve transplanting bone tissue from other species like bovine.
However, use of xenografts in Bone
Graft and Substitutes procedures is still limited in Latin America due
to high cost and perceived risks of disease transmission or immune reactions.
Also, xenografts lack osteoinductive potential. Research is still ongoing to
develop decellularized or chemically-treated xenograft products that provide an
off-the-shelf alternative with reduced immune response.
Synthetic Bone Graft Substitute Market Expanding Rapidly
With limitations and risks involved with biological grafts, synthetic bone
graft substitutes offer an attractive option. They eliminate risks of disease
transmission and immune reactions. Popular synthetic graft materials used
include calcium phosphate ceramics like hydroxyapatite and beta-tricalcium
phosphate, bioactive glass, polymers, and composites. Mexico and Brazil have
emerged as major producers and consumers of synthetic bone graft substitutes in
Latin America. The market for these products is growing at over 5% annually
driven by increasing orthopedic surgeries and awareness.
Demineralized Bone Matrix Leading
Organic Substitute
Among organic bone graft substitutes, demineralized bone matrix (DBM) obtained
from processed allografts enjoys maximum popularity and usage in Latin America.
It provides osteoinductive growth factors that stimulate new bone formation.
DBM can be mixed with other graft materials and osteoconductive carriers to
enhance its handling properties and bone ingrowth potential. DBM puts to use
otherwise discarded bone material and avoids need for additional harvesting
unlike autografts. Its ability to heal complex fractures and non-unions has
driven increased DBM adoption.
Stem Cells Open New Vistas in
Regenerative Medicine
Stem cell therapy holds promise for developing next generation biologic bone
substitutes. Mesenchymal stem cells obtained from bone marrow aspirate or
adipose tissue can be cultured and delivered to fracture sites to aid
regeneration. Clinical studies show stem cells aid fracture healing by
differentiating into osteoblasts and inducing angiogenesis. While stem cell
therapy for bone repair is still under research, its potential is being tapped.
Countries like Mexico, Brazil and Chile are active in this area and stem cell
based products may emerge in future to complement or replace existing graft
materials.
Developing New Evaluation Standards
To advance the field of bone grafting and ensure patient safety, countries in
Latin America are working to develop standardized tests and guidelines to
evaluate efficacy and performance of various bone graft substitutes. Factors
like osteoconductivity, osteoinductivity, immunogenicity, shelf-life, handling
properties, absorption/resorption rates need systematic study. Adopting
internationally accepted standards will also boost intra-regional and global
trade of these products. Regional partnerships are being formed between
industry and academia to fund more clinical research and product development
activities.
Get More Insights on Bone Grafts and Substitutes


Comments
Post a Comment