What is Veterinary Blood Glucose Levels?
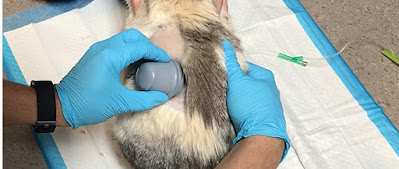 |
| Veterinary Blood Glucose |
Just like humans, glucose, commonly known as blood sugar, is the primary source of energy for pets. It is vital for cellular metabolism and overall health. Maintaining healthy and balanced blood glucose levels is important for dogs and cats. Testing blood glucose helps veterinarians diagnose and monitor conditions related to glucose metabolism.
What are normal blood glucose levels?
The normal range of blood glucose levels may vary slightly between veterinary
labs and also depends on whether the animal is fasting or not. In general, here
are the normal reference ranges:
- Dogs (fasting): 70-120 mg/dL
- Dogs (non-fasting): 80-140 mg/dL
- Cats (fasting): 75-140 mg/dL
- Cats (non-fasting): 80-180 mg/dL
Measuring Veterinary
Blood Glucose provides vets with valuable insight into a pet's overall
health and helps diagnose related medical conditions. Maintaining levels within
the normal range is crucial.
Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)
Hypoglycemia, characterized by abnormally low blood glucose levels, can occur
in pets due to various reasons like lack of food intake, liver disease,
insulinoma (a pancreatic tumor) and certain medications. Clinical signs can
include weakness, seizures, pale gums, vomiting and confusion. Treatment
focuses on addressing the underlying cause and providing supplemental dextrose
or foods to raise blood sugar levels. Untreated hypoglycemia can progress to
coma.
Diabetes Mellitus
This metabolic disorder results in high blood glucose levels when the body
cannot produce or properly use insulin, an important hormone required to
transport sugar into cells. Diabetes is very common in cats and can also affect
dogs. Clinical signs include excessive thirst, urination, weight loss despite
good appetite and lethargy. Treatment options for pets include insulin
injections, oral medications and careful diabetic diet management. Left
unmanaged, it can cause many serious health complications.
Monitoring Blood Glucose at Home
Owners of diabetic pets need to regularly monitor blood glucose levels at home
to effectively manage the disease. Veterinarians prescribe glucometers and test
strips calibrated for animal use. Blood is usually taken from a small nick made
in the inner ear or use a special lancet. Home testing helps owners gauge
insulin dose needs and provides a snapshot of how diet and medications affect
levels. It allows adjustment of treatment as needed. Together with the vet,
this key monitoring tool helps improve pet's quality of life.
Nutrition and Exercise Considerations
A balanced diet tailored to a pet's needs plays an important role in keeping
glucose levels in check. For example, weight management through portion control
and activity is important since excess weight can negatively impact insulin
sensitivity. Several high-quality commercial prescription diets are now
available for pets with diabetes, obesity or other metabolic disorders. Limited
access to treats and table scraps is also recommended as unscheduled feastings
can disrupt levels. Meanwhile, regular light exercise helps utilize glucose and
provides cardiovascular benefits to overall health.
Preventive care is key. Though blood sugar disorders can develop due to genetic
predisposition in dogs, creating a nourishing lifestyle through nutrition, exercise
and veterinary guidance helps minimize future risks. Owners should also be
educated on recognizing early clinical signs so conditions are promptly
addressed. With proper care and management, affected pets are now living
happily for many years with improved glucose balance.
Get More Insights on Veterinary Blood Glucose


Comments
Post a Comment